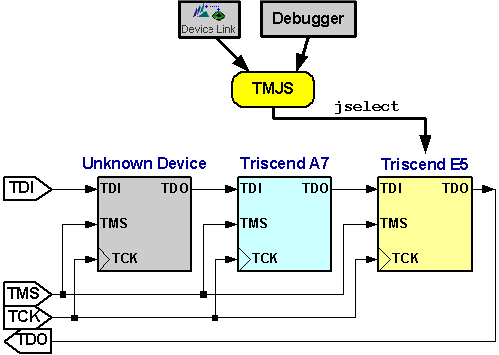
|
Can I Daisy-chain Multiple E5 or A7 Devices With new capabilities in FastChip 2.3.0, it is indeed possible to download and debug an E5 or A7 CSoC device even when it is part of a multi-device JTAG daisy-chain. FastChip 2.3.0 and later includes the Triscend MutliJTAG Server (TMJS) which allows you to specify the JTAG chain in your application and to select a specific Triscend device on the chain to download or debug. Figure 1. An example JTAG chain with three devices, connected via TMJS. Figure 1 shows an example JTAG chain with three devices. The second and third devices in the chain are Triscend CSoC devices. The first is from another vendor. The TMJS server allows a client application, like FastChip Device Link (FDL) or your source-level debugger to communicate directly with the selected Triscend device on the chain. The TMJS command jselect allows you to select a specific device. The TMJS jdetect detects and lists the devices on the chain. To handle any non-Triscend devices on the chain, TMJS requires some additional JTAG information. TMJS must know the length of the JTAG instruction register (IR) of all devices in the JTAG chain before it can scan the chain correctly. To specify a non-Triscend device, perform the following steps.
C:\Triscend\FastChip\bin
Each device description has the following format. JTAG_ID,IR_BITLEN,NAME The JTAG_ID must match the device’s JTAG identifier code (IDCODE) if it has one. If it has none or the code is unknown, use 0x0. The IR_BITLEN value specifies the number of bits in the device’s JTAG instruction register (IR). This value is critical and must be correct. The NAME field is a user-defined label and can be from 1 to 31 ASCII characters long.
The following example lists two non-Triscend devices. 0x0,5,MyUnknownDevice 0x27790061,4,SHARP_ARM7
TMJS first attempts to match up unknown devices with the user specified ID codes. Then, it assigns non-Triscend devices using the devices specified in jtaglist.tjd, starting with the first device in the chain. The first device is where the TDI JTAG signal enters the chain, which is the device on the left in Figure 1. The last device is where the TDO JTAG exits the chain, or the right-most device.
© 2002 by Triscend Corporation. All rights reserved. |